INDIAN ARMED FORCES CHIEFS ON OUR RELENTLESS AND FOCUSED PUBLISHING EFFORTS

The insightful articles, inspiring narrations and analytical perspectives presented by the Editorial Team, establish an alluring connect with the reader. My compliments and best wishes to SP Guide Publications.

"Over the past 60 years, the growth of SP Guide Publications has mirrored the rising stature of Indian Navy. Its well-researched and informative magazines on Defence and Aerospace sector have served to shape an educated opinion of our military personnel, policy makers and the public alike. I wish SP's Publication team continued success, fair winds and following seas in all future endeavour!"

Since, its inception in 1964, SP Guide Publications has consistently demonstrated commitment to high-quality journalism in the aerospace and defence sectors, earning a well-deserved reputation as Asia's largest media house in this domain. I wish SP Guide Publications continued success in its pursuit of excellence.
- MoD initiates comprehensive review of Defence Acquisition Procedure 2020, pushes for defence reforms
- G7: The Swansong
- Kalinga Connect: South Asia to Polynesia
- Must Credit DRDO for Operation Sindoor, now what is next for defence R&D?
- The layered Air Defence systems that worked superbly, the key element of Operation Sindoor
- Operation Sindoor | Day 2 DGMOs Briefing
- Operation Sindoor: Resolute yet Restrained
A Sneak Peek of Future Warfare
An overview of some of the most promising advancements in land-based weaponry that will significantly impact the modern battles

In the rapidly evolving landscape of military technology, advanced weapon systems for land forces are taking centre stage. These cutting-edge technologies promise to revolutionise warfare by providing unprecedented advantages over conventional weapons. From Directed Energy Weapons (DEWs) to Precision-Guided Missiles (PGMs) and beyond, these systems are poised to redefine the capabilities of ground-based forces.
Unmanned Combat Ground Vehicles (UCGVs)
UCGVs represent a category of unmanned land-based vehicles engineered to execute military operations autonomously, devoid of human intervention. These vehicles can be armed with an assortment of weaponry, including machine guns, grenade launchers, and missiles, and can also be equipped with various sensors like cameras and radar to augment situational awareness. The advantages of UCGVs over traditional manned vehicles are manifold:
- Reduced Risk of Casualties: UCGVs can undertake perilous tasks without exposing human soldiers to potential harm.
- Heightened Capabilities: UCGVs can be armed with weapons and sensors that might be impractical or dangerous to deploy on manned vehicles.
- Enhanced Flexibility: UCGVs can be deployed in locations inaccessible to manned vehicles, such as confined spaces like tunnels or densely populated areas.
- Reconnaissance: UCGVs could function as scouts, surveying terrain ahead of friendly forces and identifying enemy positions.
- Surveillance: UCGVs could be employed to monitor enemy activities and positions.
- Target Acquisition: UCGVs could identify and track enemy targets, contributing valuable intelligence to the operation.
- Fire Support: Armed with weaponry, UCGVs could provide crucial fire support to friendly forces by engaging enemy targets.
- Minefield Clearance: UCGVs could be tasked with clearing minefields ahead of advancing friendly forces.
UCGVs hold the potential to significantly impact modern warfare by providing armed forces with a versatile tool to conduct operations with enhanced safety and efficiency. As UCGV technology continues to advance, an increasingly pivotal role in military operations worldwide will be played by them.
Remote Controlled Weapon Stations (RCWS)
RCWS are remotely operated weapon systems equipped with a diverse array of weapons, including machine guns, grenade launchers, and missiles. They find application on various platforms such as vehicles, buildings, ships, and other installations. Advantages of RCWS over conventional weapon systems encompass:
- Enhanced Gunner Protection: RCWS enable operators to engage targets from a secure location, diminishing exposure to enemy fire.
- Heightened Accuracy: Equipped with advanced fire control systems, RCWS bolster accuracy, especially at extended ranges.
- Augmented Situational Awareness: Often integrated with sensors, RCWS afford operators a comprehensive view of their surroundings, enhancing situational awareness.
- Reduced Crew Requirements: RCWS can reduce the number of personnel required to operate a vehicle, allowing crew members to undertake additional tasks.
In military and law enforcement domains, RCWS are gaining prominence, being mounted on an array of vehicles like tanks, armoured personnel carriers, infantry fighting vehicles, and patrol boats. Additionally, they are deployed in stationary capacities, such as guard towers and checkpoints.
Recent advancements in RCWS technology encompass:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI is being harnessed to develop RCWS capable of autonomously tracking and engaging targets.
- Integration of Laser Weapons: Laser systems are being integrated into RCWS, expanding their capacity to engage targets at extended ranges.
- Size and Weight Reduction: Ongoing efforts are focused on making RCWS more compact and lightweight, rendering them suitable for an even broader range of platforms.
RCWS possess the potential to change the battlefield by affording operators the capability to engage targets from a secure location, coupled with advanced fire control systems that significantly enhance the accuracy and lethality of weapon systems.
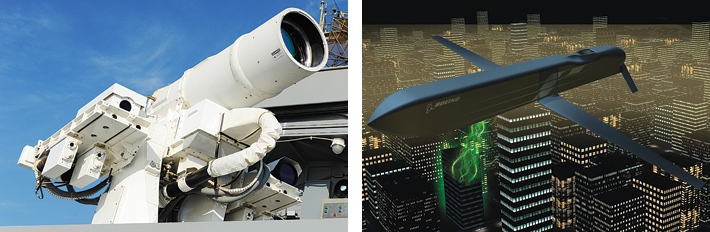
Directed Energy Weapons (DEWs)
Directed energy weapons (DEWs) employ focused energy forms like lasers, microwaves, and particle beams to damage or destroy targets. They are known for their exceptional speed, operating at the speed of light, making them effective against fastmoving targets like ballistic missiles. DEWs are highly accurate, ensuring specific target engagement while minimising collateral damage. Despite their advantages, DEWs face challenges related to power requirements, susceptibility to atmospheric conditions, and safety concerns due to handling high voltages and currents.
Laser Weapons
Laser weapons represent a pinnacle of modern military technology. Harnessing highly focused energy in the form of lasers, they promise unparalleled speed, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness. Currently in their early stages of development, laser weapons have shown potential in intercepting fast-moving targets like drones and ballistic missiles. One notable example is the US Navy’s LaWS system, designed for countering small boats and drones.
High-Powered Microwave (HPM) Weapons
HPM weapons utilise intense microwaves to incapacitate electronic systems. These weapons have the potential to disable enemy drones, aircraft, and ships, enhancing the strategic capabilities of land forces. The CHAMP system being developed by the US Army is a prime example, intended for use against enemy drones and communications systems.
Particle Beam Weapons
Utilising directed beams of charged particles, particle beam weapons hold significant promise in terms of power and effectiveness. Although still in early stages of development, they offer the potential for formidable land-based weaponry.
Advantages of DEWs
- DEWs operate at the speed of light, making them ideal for intercepting fast-moving targets like ballistic missiles.
- They exhibit high precision even over long distances, enabling specific target engagement and minimising collateral damage.
- DEWs do not rely on expensive propellants, reducing operational and maintenance expenses.
Precision-Guided Missiles (PGMs)
Precision-guided missiles (PGMs) are equipped with guidance systems that ensure accurate target strikes, utilising methods such as laser, GPS, infrared, and radar guidance. They stand out for their exceptional accuracy even at extended ranges, making them suitable for precision strikes. PGMs are often more lethal than conventional missiles due to their precise targeting, and they have a longer reach, allowing them to engage targets deep within enemy territory. However, they tend to be pricier and more complex, which leads to higher maintenance and operational demands. Additionally, PGMs using GPS or radar guidance can be vulnerable to jamming.
Advantages of PGMs
- PGMs demonstrate exceptional accuracy, even at extended ranges, making them suitable for precision strikes.
- They are often more lethal than conventional missiles due to their precise targeting.
- PGMs can have a longer reach, allowing them to engage targets deep within enemy territory.
Challenges
PGMs tend to be pricier compared to conventional missiles, they are more intricate, which can lead to higher maintenance and operational demands and since PGMs use GPS or radar guidance, they can be vulnerable to jamming.
Loitering Munitions
Loitering munitions, also known as suicide drones, are unmanned aerial systems with a built-in warhead. They hover over a target area until a suitable target is located, then engage by crashing into it. These munitions are highly accurate, capable of precise target strikes over long ranges. They are also cost-effective to produce. However, they can be affected by jamming, especially those using GPS or radar guidance.
Advantages of Loitering Munitions
- Highly accurate, capable of precise target strikes over long ranges.
- High lethality due to accurate targeting.
- Capable of reaching targets deep within enemy territory.
- Relatively cost-effective to produce. However, GPS or radar-guided loitering munitions can be affected by jamming.
Precision-Guided Firearms (PGFs)
Precision-Guided Firearms (PGFs) are longrange rifle systems utilising advanced technology to significantly improve accuracy. They incorporate features like target tracking, heads-up display for real-time information, and advanced fire control for automatic firing solutions calculation.
Key Features of PGFs
- Utilises sensors for precise target tracking.
- Provides real-time information like distance, wind speed, and elevation.
- Automatically calculates firing solutions based on various parameters.
Smart Firearms
Smart firearms integrate technology for enhanced safety and performance, utilising biometrics, RFID, and GPS for authentication and tracking. They offer increased safety by preventing unauthorised use, improved performance through enhanced accuracy and lethality, and potential crime reduction by making tracking of weapons easier.
Advantages of Smart Firearms
- Prevents unauthorised use, reducing accidental shootings and suicides.
- Enhanced accuracy and lethality through advanced technology.
- Potential to reduce gun violence and make tracking of stolen weapons easier.
Intelligent Bullets
Intelligent bullets are projectiles equipped with sensors and guidance systems to accurately track and hit targets. They offer increased accuracy, reduced risk of collateral damage, and reduced risk of friendly fire. However, they may be more expensive than conventional bullets and may have reliability variations due to being a newer technology.
Advantages of Intelligent Bullets
- Enhanced accuracy, especially at extended ranges.
- Precise targeting minimises unintended damage.
- Can distinguish between friendly and enemy forces.
Challenges
- Likely to be more expensive than conventional bullets.
- More intricate, potentially requiring higher maintenance and operational expertise.
- Being a newer technology, reliability may vary.
Exoskeletons
Exoskeletons are wearable robotic devices designed to assist or enhance human movement, with applications in rehabilitation, military, construction, manufacturing, logistics, and personal use. In military applications, exoskeletons provide increased strength and endurance, support in carrying heavy loads, enhanced protection, and improved mobility in combat scenarios. They also offer improved situational awareness through integrated sensors and displays.

Military Applications of Exoskeletons
- Increased Strength and Endurance and supports soldiers in carrying heavy loads and navigating difficult terrain.
- Provides additional armour and weapons, enhancing soldier safety.
- Enables faster and more agile movement in combat scenarios.
- Improved Situational Awareness since it is equipped with sensors and displays for real-time information about the surroundings.
Stealth and Camouflage
Stealth and camouflage are pivotal for land-based weapon systems to evade detection by adversaries. Stealth involves reducing a weapon system’s visibility to radar, infrared, and other sensors, while camouflage enables it to blend seamlessly with its surroundings.
Methods for Achieving Stealth and Camouflage Include
- Shape Optimisation: Stealthy systems are meticulously designed to minimise their radar cross-section (RCS), which measures how much radar energy is reflected. Camouflaged systems are shaped to seamlessly blend into their environment.
- Radar-Absorbent Materials (RAM): These specialised materials absorb radar energy, thereby reducing the RCS of a weapon system.
- Infrared Signature Reduction: Stealthy systems are engineered to diminish their infrared signature, i.e., the heat they emit. Camouflaged systems aim to match their infrared signature with the surrounding environment.
- Netting and Other Materials: Various materials, including netting, can be deployed to obscure weapon systems, making them less conspicuous.
- Natural Materials: Elements like branches and leaves are employed to conceal weapon systems, ensuring they harmonise with their environment.
Stealth and camouflage fortify land-based weapon systems, enhancing their effectiveness in combat scenarios. As stealth and camouflage technology continues to advance, it is anticipated that it will have even more effective applications for land-based weapon systems in the future.
Conclusion
The landscape of advanced weapon systems for land forces is rapidly evolving, promising unparalleled advantages in speed, accuracy, and lethality. From directed energy weapons to precisionguided missiles and intelligent bullets, these technologies are set to redefine the capabilities of ground-based forces. Coupled with innovations in exoskeletons, stealth, and camouflage, the future of warfare holds immense promise for land forces worldwide. As these technologies continue to advance, we can anticipate a paradigm shift in military strategy and tactics.





